Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazami; Ogiwara, Norio*; Kuramochi, Masaya*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 21(4), p.359 - 364, 2023/07
In recent years, durable target is required according to increase of the beam power. To solve this problem, a liquid film was formed in vacuum and tested it as a target. An ethanol and a mercury were selected as liquid target materials, and we investigated whether the liquid sheet could be formed stably in a vacuum and how about the vacuum pressure. As a result, it was confirmed that the liquid films were stably formed in both case and the pressures with the films were about the vapor pressure of the materials.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-036, 115 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Investigation of environment induced property change and cracking behavior in fuel debris" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to investigate the environment induced property change and cracking behavior in fuel debris from the viewpoints of materials science. The research objective is cracking behavior in fuel debris which is presumed to be influenced by environment during long-term fuel debris processing period. The degradation models will be established to simulate the oxidation and hydrogenation processes possibly occurred at fuel debris. The evolution of phase constitution and the corresponding property change in the simulated fuel debris under various environmental conditions …
Saito, Tatsuo; Yamazawa, Hiromi*; Mochizuki, Akihito
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 255, p.107035_1 - 107035_14, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)The seasonal variation of dissolved U (DU) in Lake Biwa was reproduced by the following model and parameter research. The introduced models are the water-DU mass balance, and the ion exchange between UO
 and H
and H on the lakeshore soil. The optimized parameters were the CEC of the lakeshore, TU as the sum of DU and AU (soil adsorbed U), kads and kdes as the first order reaction rate coefficients during rapid soil adsorption and desorption of U, respectively. Tabulated by the chemical equilibria constituting DU and analyzed the contribution of each chemical species, it is shown that the seasonal variation of DU is caused by the seasonal variation of pH. A correction to the ion-exchange equilibrium to shift to first order rate reaction only when the daily AU ratio increased above kads or decreased below kdes, improved the reproducibility of DU measurements and reproduced the delay of the DU peak from the pH peak.
on the lakeshore soil. The optimized parameters were the CEC of the lakeshore, TU as the sum of DU and AU (soil adsorbed U), kads and kdes as the first order reaction rate coefficients during rapid soil adsorption and desorption of U, respectively. Tabulated by the chemical equilibria constituting DU and analyzed the contribution of each chemical species, it is shown that the seasonal variation of DU is caused by the seasonal variation of pH. A correction to the ion-exchange equilibrium to shift to first order rate reaction only when the daily AU ratio increased above kads or decreased below kdes, improved the reproducibility of DU measurements and reproduced the delay of the DU peak from the pH peak.
Ando, Masaki; Saito, Kimiaki
JAEA-Technology 2021-032, 66 Pages, 2022/03
Since the occurrence of the accident at the TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a series of car-borne survey over a wide area in the eastern part of Japan using the monitoring system KURAMAII. In this report, outline of the car-borne surveys are summarized and the following characteristics of the temporal changes in each prefecture and region were investigated using the measured data obtained from 2012 to 2019; 1) Average and maximum values for each prefecture for the six years from 2014 to 2019, 2) Average values for each prefecture from 2012 to 2019, 3) Average values for each evacuation order area category, regional category, and northern Soso-area municipality in Fukushima Prefecture from 2012 to 2019, and 4) Average and maximum values for each municipality in each prefecture for four times (at almost two-year intervals) of the measurement results from 2012 to 2018.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2021-058, 75 Pages, 2022/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Investigation of environment induced property change and cracking behavior in fuel debris" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to investigate the environment induced property change and cracking behavior in fuel debris from the viewpoints of materials science. The research objective is cracking behavior in fuel debris which is presumed to be influenced by environment during long-term fuel debris processing period. The degradation models will be established to simulate the oxidation and hydrogenation processes possibly occurred at fuel debris.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Tsukahara, Takehiko*; Brandt, A.*; Muto, Yuki*; Nabatame, Nozomi*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Sciences, 37(12), p.1789 - 1794, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.35(Chemistry, Analytical)We attempted to scale down a separation process of uranium (U) using the microchip column loaded with anion exchange resin to develop safety and waste-reducing separation technique. The ideal separation performance of U was obtained by the properly design of a microchannel. The concentration of U in seawater as a real-world sample could be quantified with the prepared microchip column. It indicates that the microchip column is sufficiently practical. Compared to separation of U with a general column, the column size was successfully scaled down to  1/5000.
1/5000.
 -treated column study of Hanford 300 area sediment using a simple ion exchange and immobile domain model
-treated column study of Hanford 300 area sediment using a simple ion exchange and immobile domain modelSaito, Tatsuo; Sato, Kazuhiko; Yamazawa, Hiromi*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 237, p.106708_1 - 106708_9, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.7(Environmental Sciences)We succeeded at numerical reproduction of dissolved U concentrations from column experiments with PO -treated Hanford 300 Area sediment. The time-series curves of dissolved U concentrations under various Darcy flow rate conditions were reproduced by the numerical model in the present study through optimization of the following parameters:(i) the mass of U in mobile domain (on surface soil connected to the stream) and the rest of the total U left as precipitation in immobile domain (isolated in deep soil);(ii) the mixing ratio between immobile and mobile domains, to fit the final recovering curve of concentration; and (iii) the cation exchange capacity (CEC
-treated Hanford 300 Area sediment. The time-series curves of dissolved U concentrations under various Darcy flow rate conditions were reproduced by the numerical model in the present study through optimization of the following parameters:(i) the mass of U in mobile domain (on surface soil connected to the stream) and the rest of the total U left as precipitation in immobile domain (isolated in deep soil);(ii) the mixing ratio between immobile and mobile domains, to fit the final recovering curve of concentration; and (iii) the cation exchange capacity (CEC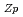 ) and equilibrium constant (k
) and equilibrium constant (k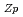 ) of the exchange reaction of UO
) of the exchange reaction of UO
 and H
and H on simulated soil surface (
on simulated soil surface (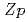 ), to fit the transient equilibrium concentration, forming the bed of the bathtub curve.
), to fit the transient equilibrium concentration, forming the bed of the bathtub curve.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Saha, P. K.; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Okabe, Kota; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Fujirai, Kosuke; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Suganuma, Kazuaki
EPJ Techniques and Instrumentation (Internet), 8(1), p.9_1 - 9_9, 2021/07
The 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex supplies a high-intensity proton beam for neutron experiments. Various parameters are monitored to achieve a stable operation, and it was found that the oscillations of the charge-exchange efficiency and cooling water temperature were synchronized. We evaluated the orbit fluctuations at the injection point using a beam current of the injection dump, which is proportional to the number of particles that miss the foil and fail in the charge exchange, and profile of the injection beam. The total width of the fluctuations was approximately 0.072 mm. This value is negligible from the user operation viewpoint as our existing beam position monitors cannot detect such a small signal deviation. This displacement corresponds to a 1.63 10
10 variation in the dipole magnetic field. Conversely, the magnetic field variation in the L3BT dipole magnet, which was estimated by the temperature change directly, is 4.08
variation in the dipole magnetic field. Conversely, the magnetic field variation in the L3BT dipole magnet, which was estimated by the temperature change directly, is 4.08 10
10 . This result suggested that the change in the cooling water temperature is one of the major causes of the efficiency fluctuation.
. This result suggested that the change in the cooling water temperature is one of the major causes of the efficiency fluctuation.
Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
Applied Clay Science, 204, p.106034_1 - 106034_13, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:99.67(Chemistry, Physical)Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 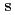 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 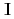 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 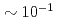 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (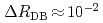 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Tominaga, Taiki*; Kobayashi, Makoto*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Matsuura, Masato*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kasai, Satoshi*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011095_1 - 011095_5, 2021/03
A vertical movement type of sample changer for the neutron spectrometer BL02, J-PARC MLF was developed for our top-loading type cryostat. The sample changer, termed as "PEACE", can control reproducibility of the irradiated position using guides made of polyether ether ketone. The variation between the background scattering profiles of three sample positions was found to be less than plus minus 1.6%. This result is reasonable, considering the deviation of sample position of less than plus minus 0.3 mm from the vertical axis.
Nishio, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Mayuko; Iyatomi, Yosuke; Hama, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Review 2020-013, 59 Pages, 2020/08
The Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting geoscientific study in order to establish a scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of HLW. Technical information of the result on the geoscientific study conducted at TGC is provided at the annual Information and Opinion Exchange Conference on Geoscientific Study of TGC for exchanging opinions among researchers and engineers from universities, research organizations and private companies. This document compiles the research presentations and posters of the conference in Mizunami on November 20, 2019.
Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Hamase, Erina; Ezure, Toshiki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00546_1 - 19-00546_11, 2020/06
Fully natural circulation decay heat removal systems (DHRSs) are to be adopted for sodium fast reactors, which is a passive safety feature without any electrical pumps. It is required to grasp the thermal-hydraulic phenomena in the reactor vessel and evaluate the coolability of the core under the natural circulation not only for the normal operating condition but also for severe accident conditions. In this paper, the numerical results of the preliminary analysis for the sodium experimental condition with the PLANDTL-2 are discussed to establish an appropriate numerical models for the reactor core including the gap region among the subassemblies and the DHX. From these preliminary analyses, the characteristics of the thermal-hydraulics behavior in the PLANDTL-2 to be focused are extracted.
Suzuki, Tomoya*; Ogata, Takeshi*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Kobayashi, Toru; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Narita, Hirokazu*
Analytical Sciences, 35(12), p.1353 - 1360, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:12.17(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Saito, Kimiaki; Mikami, Satoshi; Ando, Masaki; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinase, Sakae; Tsuda, Shuichi; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Sato, Tetsuro*; Seki, Akiyuki; Yamamoto, Hideaki*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105878_1 - 105878_12, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:80.86(Environmental Sciences)Mikami, Satoshi; Tanaka, Hiroyuki*; Matsuda, Hideo*; Sato, Shoji*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Suzuki, Takeo*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Ando, Masaki; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105941_1 - 105941_12, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:66.33(Environmental Sciences)The deposition densities of radiocesium and the air dose rates were repeatedly measured in a large number of undisturbed fields within the 80km zone that surrounds the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant site between 2011 and 2016, and features of their temporal changes were clarified. The average air dose rate excluding background radiation in this zone decreased to about 20% of the initial value during the period from June 2011 to August 2016, which was essentially a result of the radioactive decay of  Cs with a half-life of 2.06y. The air dose rate reduction was faster than that expected from the decay of radiocesium by a factor of about two, with most of this reduction being attributed to the penetration of radiocesium into the soil. The average deposition densities of
Cs with a half-life of 2.06y. The air dose rate reduction was faster than that expected from the decay of radiocesium by a factor of about two, with most of this reduction being attributed to the penetration of radiocesium into the soil. The average deposition densities of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs in fields that were not decontaminated were found to have decreased nearly according to their expected radioactive decay, which indicated that the movement of radiocesium in the horizontal direction was relatively small. The effect of decontamination was apparently observed in the measurements of air dose rates and deposition densities. Nominally, the average air dose rates in the measurement locations were reduced by about 20% by decontamination and other human activities, of which accurate quantitative analysis is and continue to be a challenge.
Cs in fields that were not decontaminated were found to have decreased nearly according to their expected radioactive decay, which indicated that the movement of radiocesium in the horizontal direction was relatively small. The effect of decontamination was apparently observed in the measurements of air dose rates and deposition densities. Nominally, the average air dose rates in the measurement locations were reduced by about 20% by decontamination and other human activities, of which accurate quantitative analysis is and continue to be a challenge.
Saito, Kimiaki; Mikami, Satoshi; Ando, Masaki; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinase, Sakae; Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tetsuro*; Seki, Akiyuki; Sanada, Yukihisa; Wainwright-Murakami, Haruko*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 44(4), p.128 - 148, 2019/12
Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Hamase, Erina; Ezure, Toshiki
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/05
Decay heat removal system (DHRS) by using the natural circulation without depending on the pump as the mechanical equipment is recognized as one of the most effective methodologies for the sodium-cooled fast reactor from the viewpoint of the safety enhancement. In this paper, the numerical simulation results of the preliminary analysis for the sodium experiment with the apparatus of PLANDTL-2, in which the core and the upper plenum with a dipped-type direct heat exchanger (DHX) were modeled, were discussed, in order to establish appropriate numerical models for the reactor core including the gap region among the subassemblies and the DHX.
Kunii, Katsuhiko; Itabashi, Keizo; Yonezawa, Minoru
JAEA-Review 2019-002, 237 Pages, 2019/03
From 1987 to 2014, the Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDE) Program under the auspices of the International Energy Agency (IEA) had been carried out successfully with fruitful outcomes. ETDE had been able to be an excellent database for use in the general field of application of energy, including nuclear energy. ETDE could have deserved it, by extensively collecting the literature and providing the metadata worldwide, as well as by delivering and disseminating the bibliographic data, first to member countries, next additionally to the developing countries free of charge and finally all the world through the Internet free of charge as well. During all the days of ETDE Program Then ETDE had been very close and strong ties and cooperation with the International Nuclear Information System (INIS) Program under the auspices of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), e.g., by sharing and complementing many elements and parts of each database mutually. A portal site, the ETDE World Energy Base (ETDEWEB), for the database of ETDE, had been available for use to deliver and disseminate the valuable information of bibliography of ETDE, containing directions to the full text data, dedicated to satisfying the interest of end users worldwide. As of today, even if the addition of bibliographic data to ETDE has ceased since 2014, ETDEWEB itself has been available as before, maintained in great help of the Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI) of the Department of Energy (DOE), US, while OSTI had been praised as the Operating Agent (OA) of ETDE Program from the commencement to the ceasing. This is a report containing several historical documents in regard with the ETDE activities worldwide kept and remained in Japan as records (minutes etc) at the side of JAERI.
Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Ikeda, Hisashi*; Shibata, Kenji*; Kokubu, Yoko; Murakami, Takuma*; Tani, Yukinori*; Takano, Masao*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Tanaka, Atsushi*; Naito, Sayuri*; et al.
Global and Planetary Change, 164, p.11 - 26, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:43.2(Geography, Physical)Paleoenvironmental and paleoclimate changes in Siberia were reconstructed by continuous, high-resolution records of chemical compositions from a sediment core retrieved from the Buguldeika Saddle, Lake Baikal, dating back to the last 33 cal. ka BP. The Holocene climate followed by a shift at ca. 6.5 cal. ka BP toward warm and dry, suggesting that the climate system transition from the glacial to interglacial state occurred. In the last glacial period, the deposition of carbonate mud from the Primorsky Range was associated with Heinrich events (H3 and H1) and the Selenga River inflow was caused by meltwater of mountain glaciers in the Khamar-Daban Range. The anoxic bottom-water during Allerod-Younger Dryas was probably a result of weakened ventilation associated with reduced Selenga River inflow and microbial decomposition of organic matters from the Primorsky Range. The rapid decline in precipitation during the early Holocene may have been a response to the 8.2 ka cooling event.